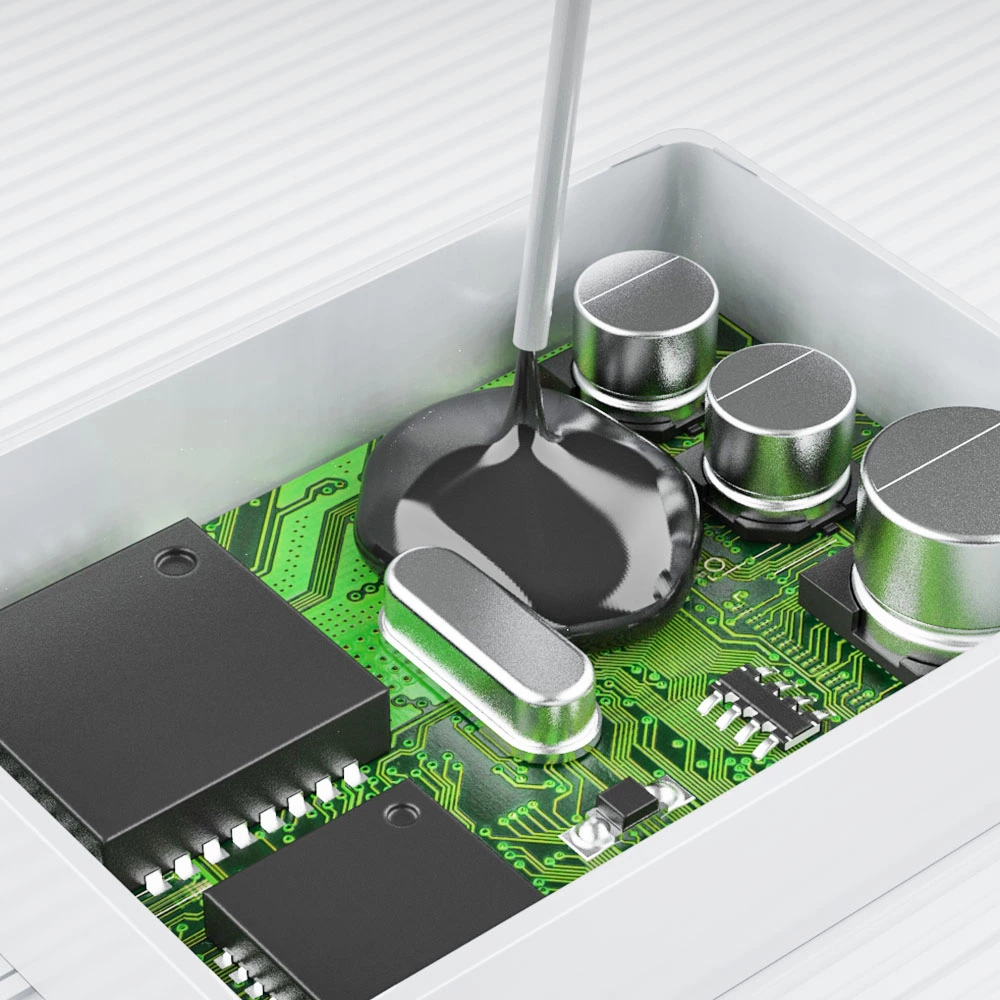
In modern electronics, efficient heat dissipation is critical for device reliability and performance. Thermal interface materials (TIMs) bridge the microscopic air gaps between uneven surfaces—such as CPUs, chips, and heat sinks—to minimize thermal resistance and maximize heat transfer efficiency. At Fehonda (Shenzhen Feihongda Technology), we specialize in advanced TIM solutions tailored for industries like automotive electronics, aerospace, and consumer devices. Below, we explore why TIMs are essential and compare key materials used today

The Necessity of Thermal Interface Materials and Common Solutions for Electronics Cooling
Why Are Thermal Interface Materials Indispensable?
Mechanical imperfections during manufacturing create microscopic gaps between components. Since air (a poor thermal conductor) occupies these voids, heat accumulates, drastically reducing cooling efficiency. TIMs fill these gaps, ensuring direct contact between surfaces and providing a continuous heat transfer path. Without TIMs, heat sinks and cooling systems would fail to function optimally, risking device overheating and premature failure.
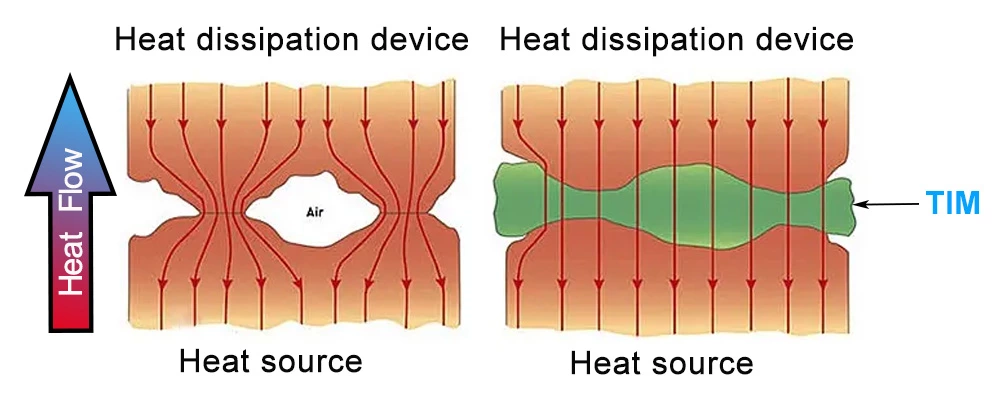
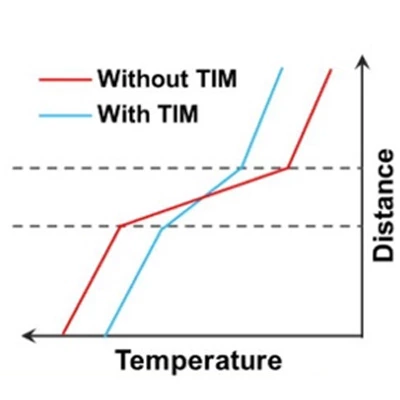
Common Thermal Interface Materials: Pros, Cons, and Applications
* Phase Change Materials (PCMs)
Fehonda’s PCMs, such as the PCM8990, transition from solid to liquid at 52°C, filling micro-gaps to achieve ultra-low thermal resistance.
Pros:
Reusable and repairable; customizable thickness/shape.
No silicone oil migration or aging issues (unlike traditional grease).
Ideal for automated processes (dispensing, printing).
UL94 V-0 flame-retardant and RoHS-compliant.
Cons:
Higher cost compared to basic greases.
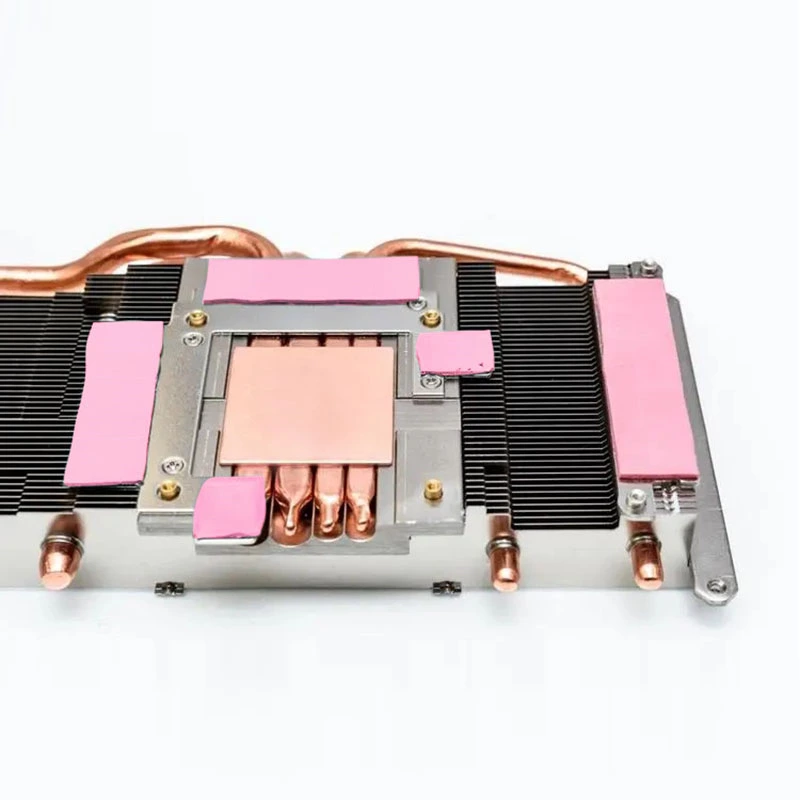
Applications: Power modules, IGBTs, memory modules, and high-reliability automotive systems.
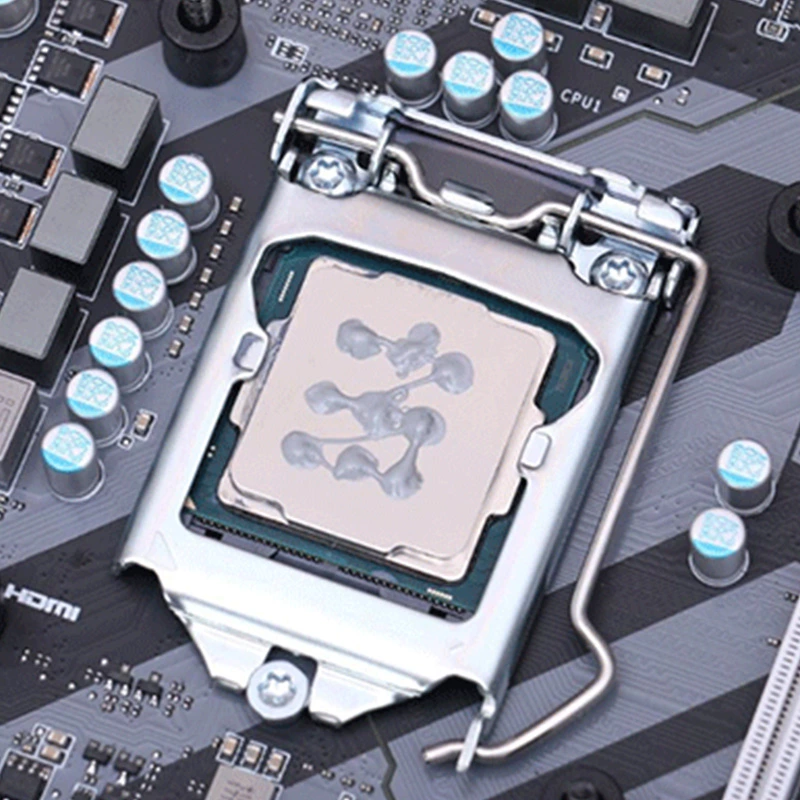
* Thermal Grease (Thermal Paste)
A cost-effective liquid TIM for high-power components.

Pros:
Excellent wettability for uneven surfaces.
High thermal conductivity (1–8 W/mK).
Waterproof and electrically insulating.
Cons:
Prone to pump-out and drying over time.
Messy application; risk of contamination.
Applications: CPUs, GPUs, and consumer electronics.
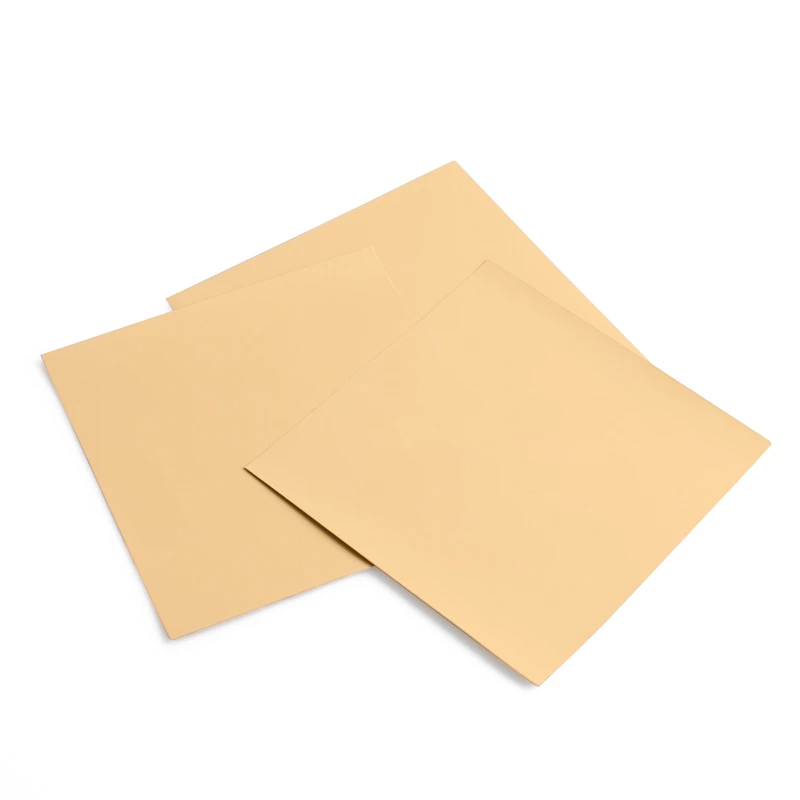
* Thermal Pads
Fehonda’s silicone-based pads offer pre-formed, compressible solutions.
![]()
Pros:
Easy installation and reusability.
Vibration damping and electrical insulation.
Stable performance under extreme temperatures (-40°C to 200°C).
Cons:
Limited by pre-set thickness; higher thermal resistance than grease.
Applications:
LED lighting, network equipment, and automotive electronics.
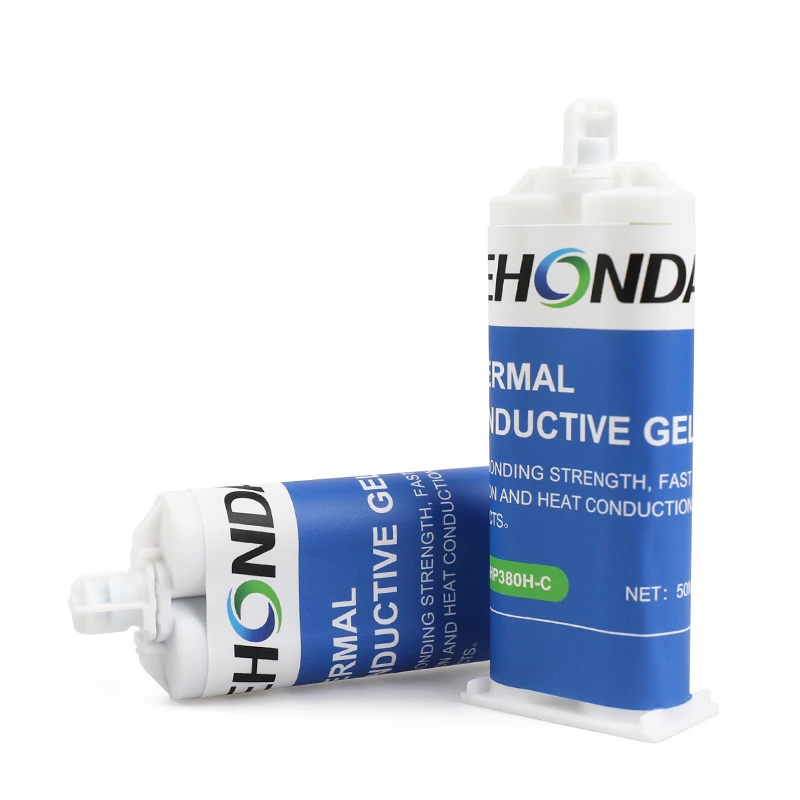
* Thermally Conductive Adhesives
Dual-purpose adhesives that bond components while dissipating heat.
![]()
Pros:
High adhesion strength and shock resistance.
Excellent dielectric properties (breakdown voltage >6,000 V/mm).
Cons:
Irreversible curing; limited gap-filling capability.
Applications:
Sensor modules, PCB components, and medical devices.
* Thermal Gap Fillers (Encapsulants)
Fehonda’s polyurethane-based gap fillers balance thermal conductivity (0.6–3 W/mK) and mechanical protection.
Pros:
Waterproofing and vibration resistance.
Easy to remove for repairs.
Cons:
Moderate thermal performance; complex curing process.
Applications:
Power supplies, inverters, and renewable energy systems.
* Thermal Tapes
Acrylic/silicone hybrid tapes for low-power applications.
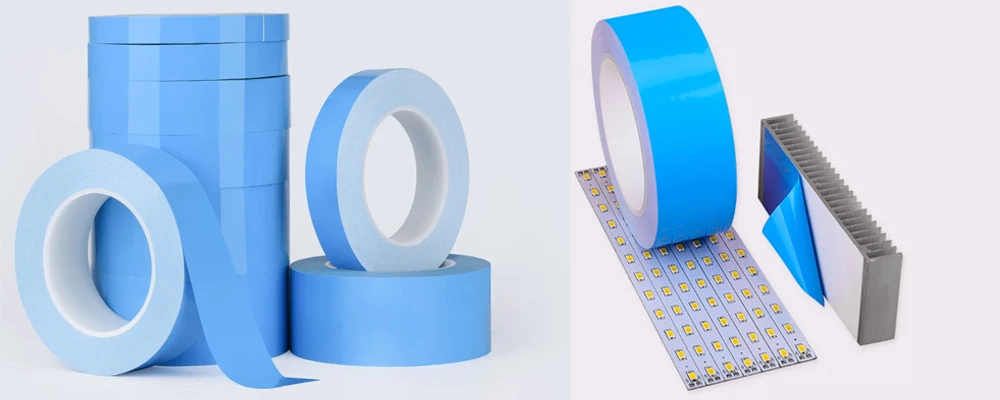
Pros:
Simple application and component fixation.
Clean, residue-free removal.
Cons:
Limited thermal conductivity (~1–3 W/mK).
Applications:
LED mounting, small heat sinks, and consumer gadgets.
Why Choose Fehonda?
As a leader in TIM innovation, Fehonda combines 17+ years of R&D expertise with ISO-certified manufacturing. Our portfolio spans:
PCMs: Optimized for high-power semiconductors and 5G infrastructure.
Custom Solutions: Tailored thickness (0.3–20 mm), shapes, and UL94 V-0 compliance.
Sustainability: RoHS-compliant materials for eco-conscious industries.
Conclusion
Selecting the right TIM depends on thermal demands, environmental conditions, and cost constraints. Fehonda’s TIMs—from phase-change sheets to high-conductivity gels—ensure optimal thermal management for next-gen electronics. Contact us for tailored solutions.







