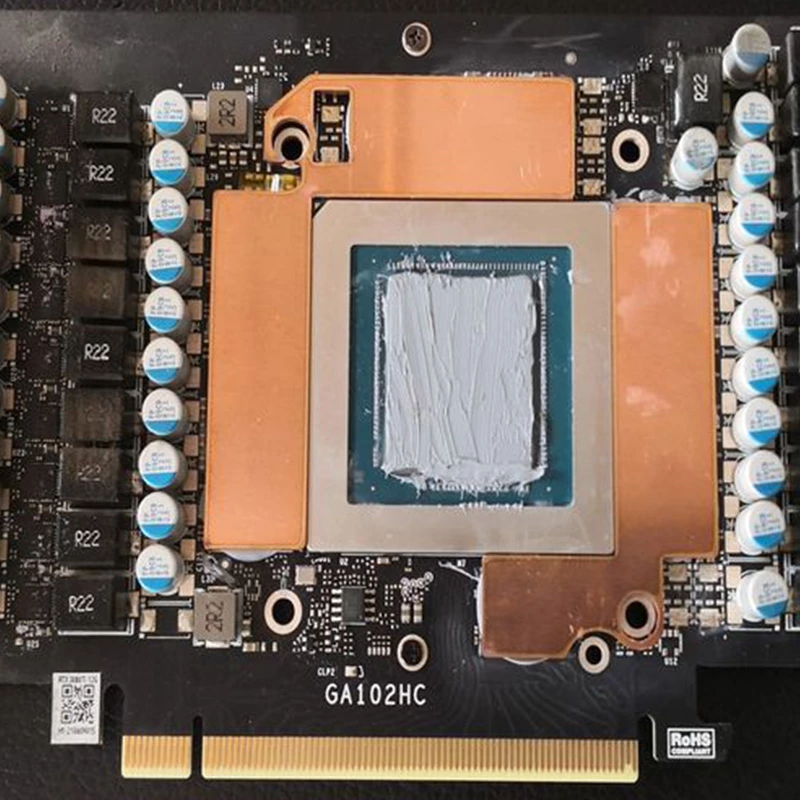
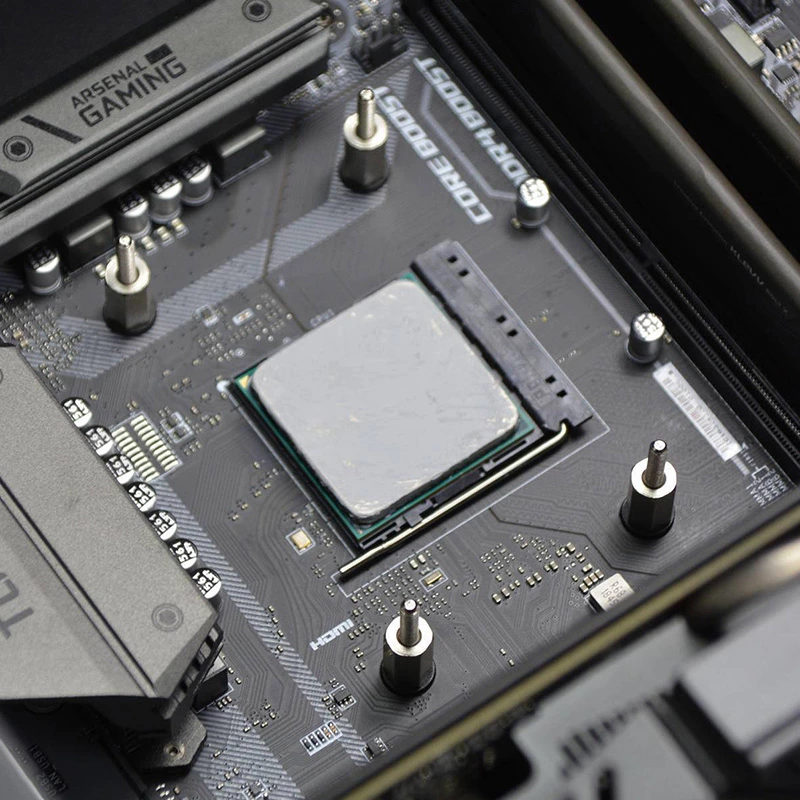
In the high-performance computing world, managing CPU heat is vital to maintaining both performance and longevity. Overheating can lead to throttling and hardware damage. One effective solution to this issue is the use of thermal conductive materials. This article explores how these materials enhance CPU cooling, the types available, and practical application tips.
CPU Thermal Solutions
Introduction
In the high-performance computing world, managing CPU heat is vital to maintaining both performance and longevity. Overheating can lead to throttling and hardware damage. One effective solution to this issue is the use of thermal conductive materials. This article explores how these materials enhance CPU cooling, the types available, and practical application tips.
Understanding CPU Heat Dissipation
CPU generates heat as it processes data, and efficient heat dissipation is crucial to prevent overheating. Key components involved in this process include:
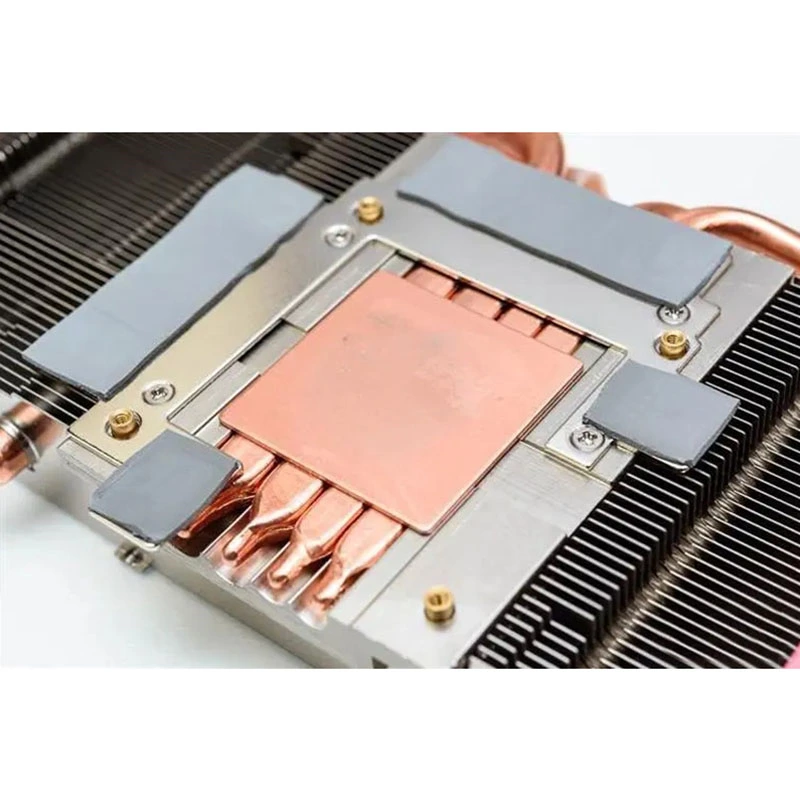
Heat Spreaders: These metal plates absorb heat from the CPU and spread it across a larger area.
Heat Sinks: Finned structures that increase the surface area for heat dissipation into the air.
Thermal Conductive Materials: These materials fill microscopic gaps between the CPU and heat spreader or heat sink, improving heat transfer efficiency.
Why Thermal Conductive Materials Matter
The CPU is the heart of any computing system, responsible for executing instructions and processing data. As it performs complex calculations, it generates heat. If this heat is not dissipated effectively, it can lead to thermal throttling, where the CPU reduces its performance to lower its temperature, or even catastrophic failure.
The Consequences of Overheating
- Performance Degradation: Excessive heat can cause the CPU to slow down to prevent damage, impacting the overall performance of the system.
- Hardware Damage: Continuous overheating can lead to permanent damage to the CPU and other components, necessitating costly repairs or replacements.
- Shortened Lifespan: Consistent exposure to high temperatures can reduce the lifespan of a CPU, leading to earlier upgrades and increased costs.
Thermal conductive materials play a crucial role in heat dissipation. Here’s why they are essential:
- Enhanced Heat Transfer: They bridge the gap between the CPU and the heat Spreader, ensuring efficient heat removal.
- Improved Performance: Effective cooling prevents thermal throttling, allowing the CPU to run at peak performance.
- Extended Hardware Lifespan: By reducing thermal stress, these materials help prevent damage and extend the life of your CPU.
Types of Thermal Conductive Materials
Several types of thermal conductive materials are used in CPU cooling. Understanding each can help you choose the best one for your needs:
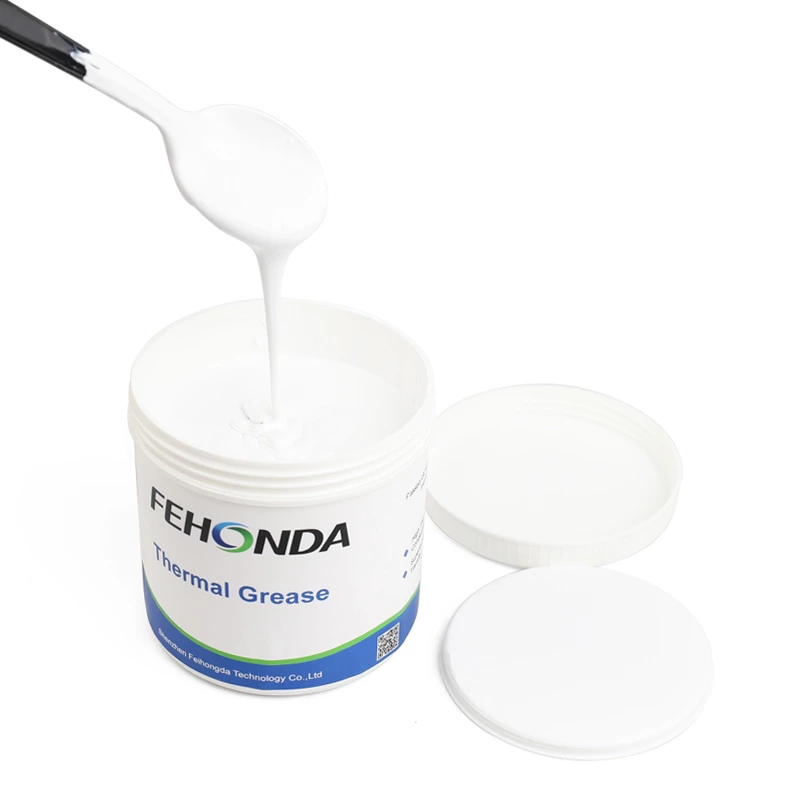
Thermal Grease (Thermal Paste)
Thermal grease, also known as thermal paste, is a viscous substance that fills microscopic air gaps between the GPU and the heatsink. It is typically made from a base material, such as silicone, and mixed with thermally conductive materials like silver, copper, or ceramic particles.
As a medium for transferring heat, thermal grease has many advantages, such as excellent thermal conductivity, good lubricity, electrical insulation, good resistance to high and low temperatures, low viscosity and good construction performance. In addition, it also has the characteristics of low usage thickness and low thermal resistance, which makes it suitable for scenarios with high heat generation and close fit. It can be used to quickly transfer heat from the device to achieve good temperature control, thereby extending the service life of electronic components and improving their reliability. It can be placed on the heating device by dispensing, printing, etc. Thermal grease is a excellent thermal conductive composite material suitable for smaller gaps or no gaps.
Features and Advantages
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda thermal grease: 1-14.8W/mK
- Excellent thermal conductivity, high stability, excellent wetting performance
- Low thermal resistance, easy construction, and a very thin interface layer can be formed on the rough surface
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental requirements


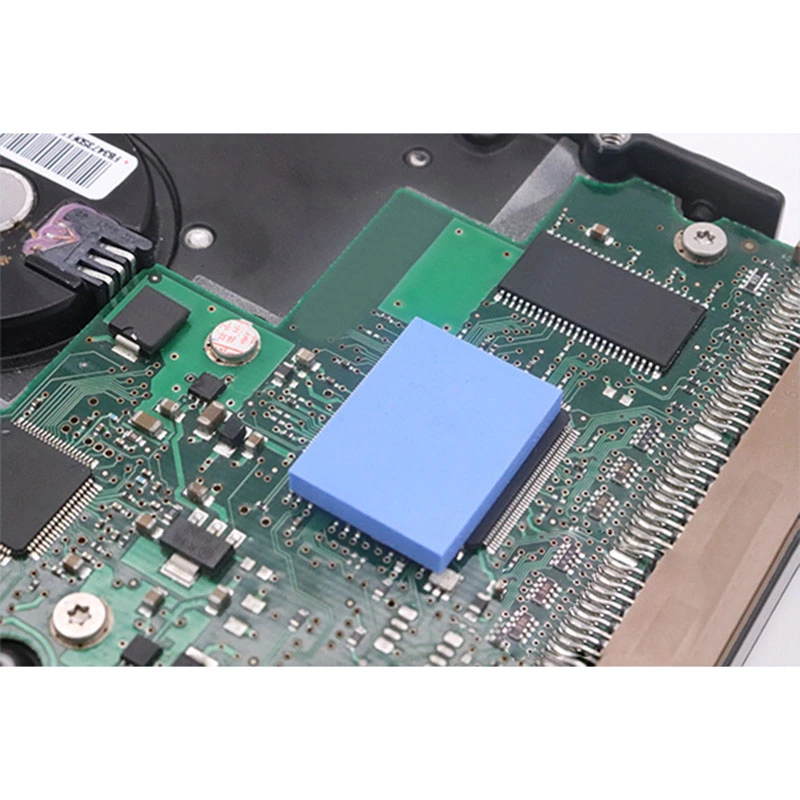
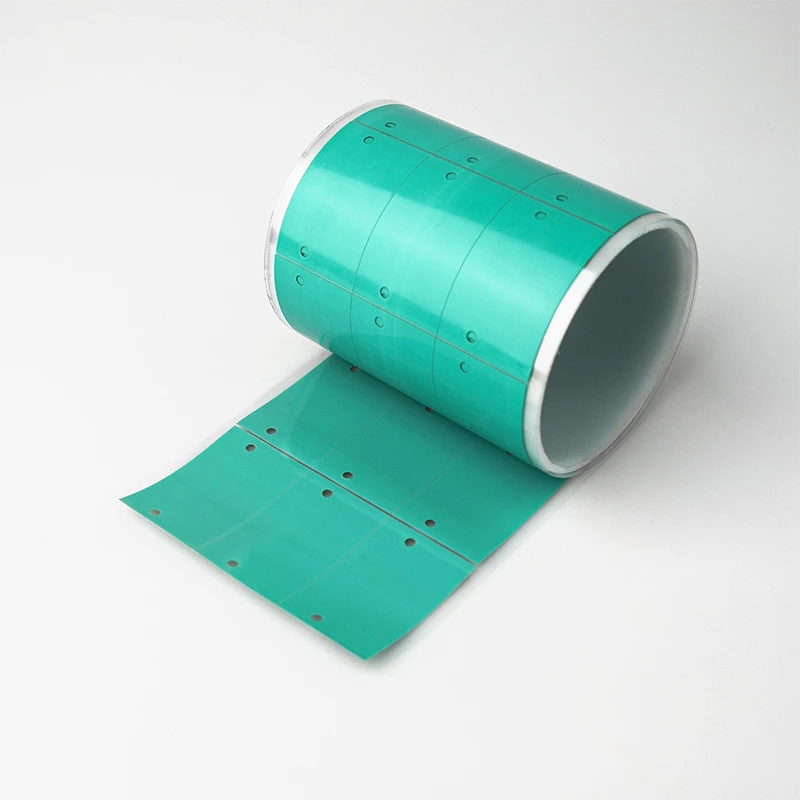
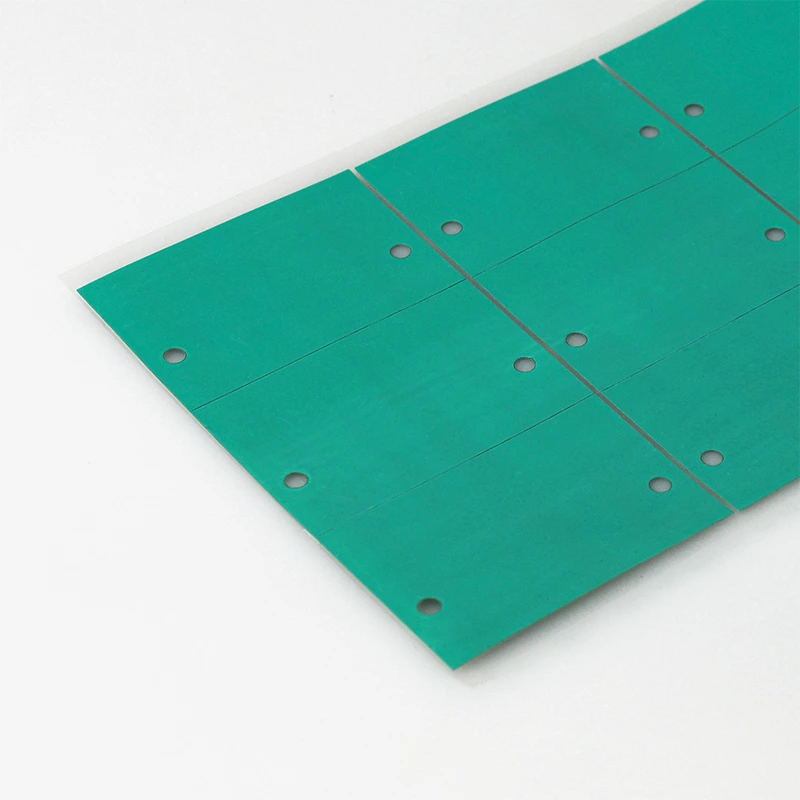
Phase Change Material (PCM)
Phase change material is a specialized thermal interface material that change the state (from solid to liquid) at a specific temperature. This phase change allows it to adapt to varying thermal conditions, providing effective heat dissipation.
Phase change material is made of nano-grade high thermal conductive filler and phase change compound. It is used for the heat transfer interface between power consumption devices and heat sinks.
The state of the material changes at 52°C, from solid to liquid. Liquid phase change material can fully wet the surface of power-consuming devices and heat sinks to form an excellent heat conduction channel. It can also be used to achieve optimal heat dissipation performance of the heat sink and enhance the reliability of power devices.
Features and Advantages
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda phase change material: 8.5W/mk
- Phase change occurs at 52℃, from solid phase to liquid phase
- Low thermal resistance, excellent thermal conductivity and heat dissipation performance, good reliability
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental protection requirements

Choosing the Right Thermal Conductive Material
Selecting the appropriate material depends on various factors:
Thermal Conductivity
The primary factor to evaluate is the thermal conductivity of the material. Materials with higher thermal conductivity ratings (measured in W/m·K) will transfer heat more effectively. Aim for materials that exceed 5 W/m·K for optimal performance.
Compatibility
Ensure the material is compatible with your CPU and cooling system to avoid any issues.
Environmental Factors
High Temperatures: If your system runs at high temperatures, choose materials designed to withstand heat without breaking down.
Cost vs. Performance
While premium thermal materials can offer better performance, balance cost with your cooling needs. For standard applications, suitable products may suffice.
Application Tips for Optimal Performance
Proper application of thermal conductive materials can significantly impact cooling efficiency:
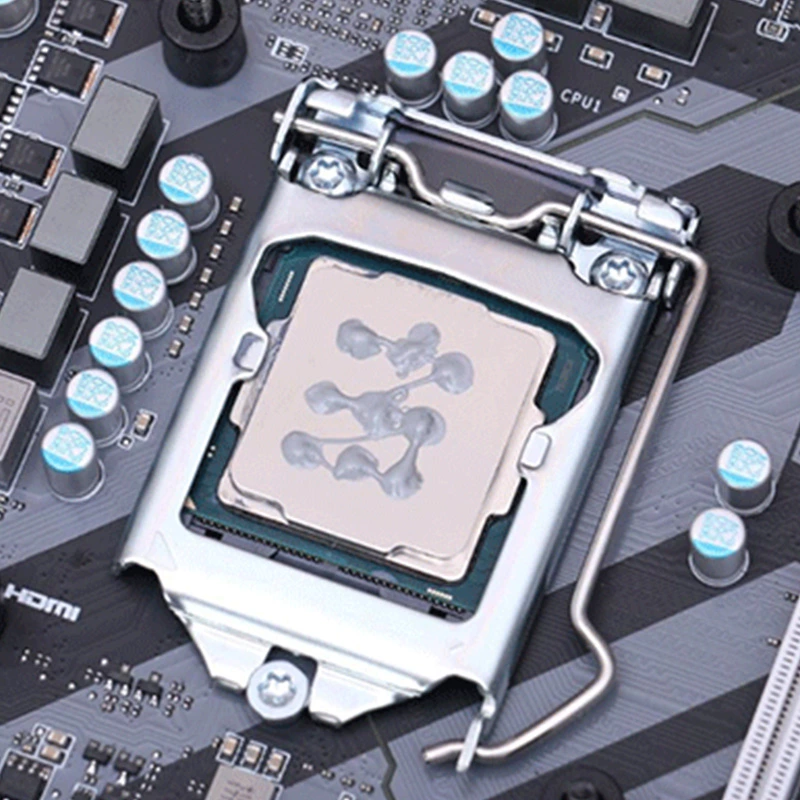
- Clean Surfaces: Before applying any material, clean both the CPU and heat sink to remove old paste or debris. Use isopropyl alcohol for best results.
- Apply Evenly: For thermal paste, a small pea-sized amount in the center of the CPU is typically sufficient. Spread it evenly if required. Thermal pads should be cut to fit the surface size precisely.
- Avoid Over-application: Excess thermal paste or adhesive can hinder performance. Apply a thin, even layer to ensure effective heat transfer.
- Maintenance and Replacement: Regularly check the condition of your thermal conductive materials, especially if you notice temperature spikes. Over time, thermal paste can dry out and lose effectiveness, so consider reapplying it as part of routine maintenance.
Conclusion
Using high-quality thermal conductive materials is a proven method for effective CPU cooling. By enhancing heat transfer, these materials help maintain peak performance and extend hardware life. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a general consumer, or an IT professional, understanding and utilizing these materials can make a significant difference in your system’s cooling efficiency. Invest in the right thermal solutions and keep your CPU running smoothly, even under intense workloads.