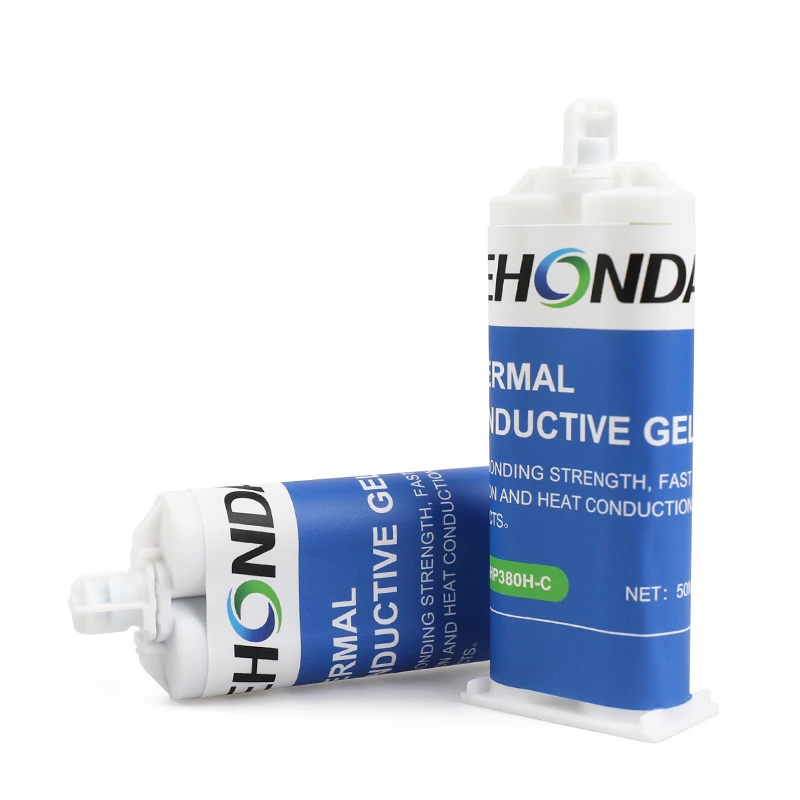
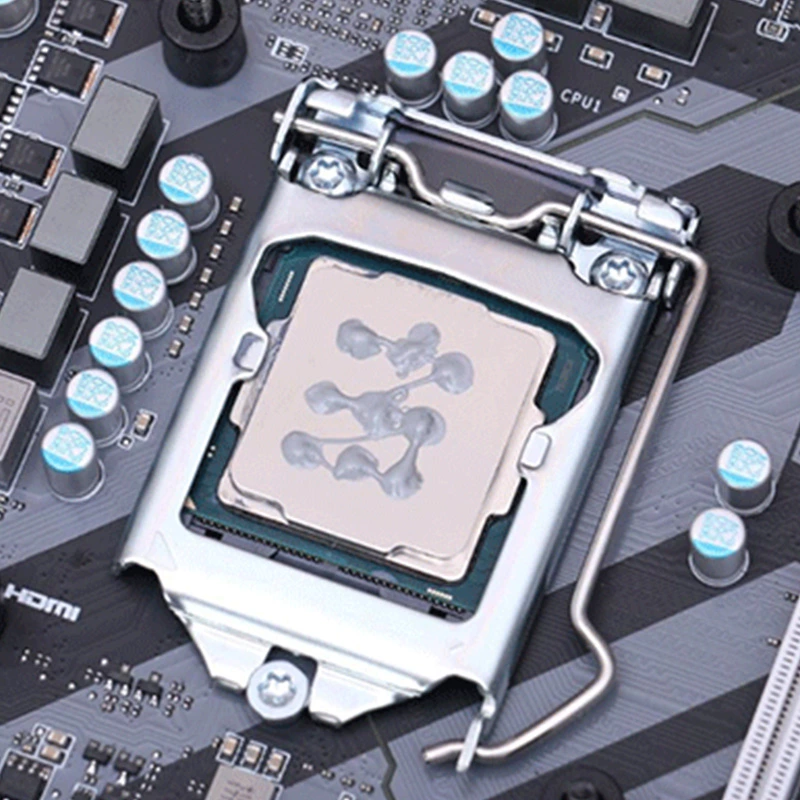
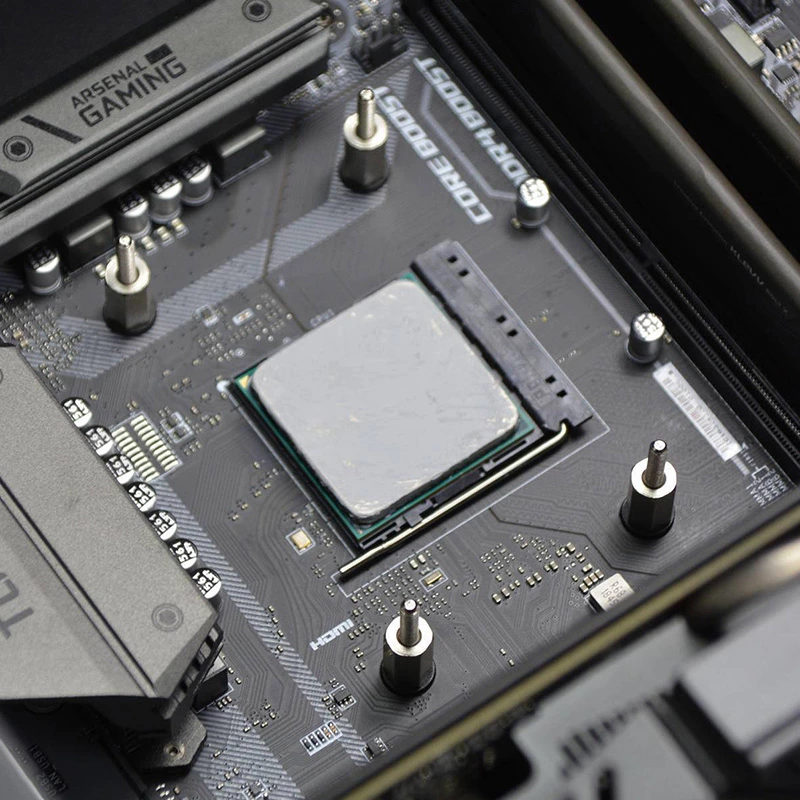
The graphics card is a very important computer accessory.
Excessive graphics card temperature will affect the speed of the computer.
Next, let's take a look at how thermally conductive materials help the graphics card cool down.
The GPU core will be coated with a layer of thermally conductive silicone grease.
The wettability can quickly fill the micropores of the interface,
greatly reducing the interface thermal resistance, so as to achieve rapid heat dissipation.
At the memory, we can add FEHONDA thermal pads to fill the gap between the cooler and the memory. They have compressibility, high reliability in long-term use and can also be customized according to different needs.
GPU Thermal Solutions
Introduction
In modern computing, GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) plays a pivotal role in rendering complex graphics and executing intensive computations. As GPU becomes increasingly powerful, it generates significant amounts of heat, necessitating effective thermal management solutions to ensure optimal performance and longevity. One of the key aspects of this thermal management is the use of thermal conductive interface materials, which include thermal pads, thermal grease, thermal gel, and other similar substances. This article delves into the various types of thermal conductive materials, their properties, applications, and how they contribute to effective GPU heat dissipation.
Understanding Thermal Conductive Interface Materials
Thermal conductive interface materials are substances used to enhance heat transfer between the GPU chip and its cooling solution, such as a heatsink or thermal plate. Their primary function is to reduce thermal resistance and improve heat dissipation, which helps in maintaining the GPU's operational temperature within safe limits.
Thermal Resistance and Conductivity
Thermal resistance is a measure of a material's ability to resist heat flow, while thermal conductivity refers to the material's ability to conduct heat. Lower thermal resistance and higher thermal conductivity are desirable traits in thermal interface materials. These properties ensure that heat is effectively transferred from the GPU to the cooling solution, minimizing the risk of overheating and performance throttling.
Selecting the right thermal interface material (TIM) for GPU cooling is crucial to ensure efficient heat dissipation and maintain optimal performance and longevity of your graphics card. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you choose the right TIM for your GPU.
Understand the Types of Thermal Conductive Interface Materials
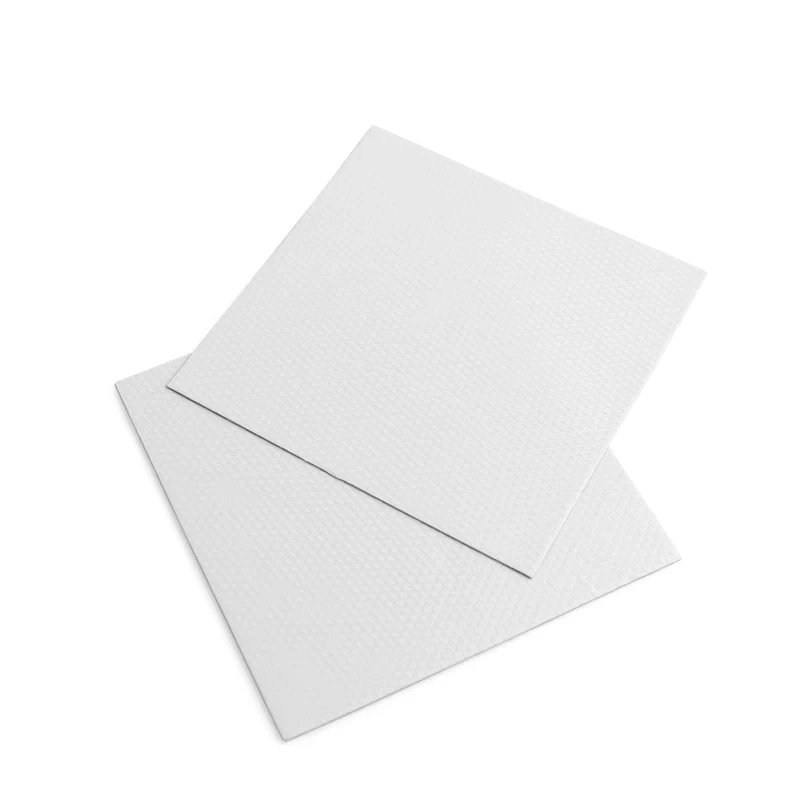
Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are pre-formed sheets or blocks of material used to fill gaps between the GPU and heatsink. They are typically made from silicone or similar polymers that are infused with thermally conductive fillers, such as aluminum oxide or boron nitride.
Thermal pads have many advantages, such as good insulation, compressibility, softness, and excellent thermal conductivity. The surface of thermal pads are sticky. They can be used to fill the gaps between the heat sources and the heat sinks and squeeze out the air to achieve full contact, so that the heat conduction between the heating parts and the heat dissipation parts can be completed efficiently. At the same time, thermal pads can play the role of insulation and shock absorption, and they can also meet the design requirements of miniaturization and ultra-thinness. In general, thermal pads are excellent thermal conductive filling materials and they are widely used in various electronic components.
Features and Advantages
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda thermal pads: 1.5-10.0W/mk
- Low thermal resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, good weather resistance
- Self-adhesive, good fit, easy to assemble
- Soft, good compressibility, high reliability in long-term use
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental protection requirements
Applications
Consumer Electronics: Widely used in laptops, desktop PCs, and gaming consoles.
Industrial Equipment: Employed in various electronic devices requiring thermal management.


Thermal Grease (Thermal Paste)
Thermal grease, also known as thermal paste, is a viscous substance that fills microscopic air gaps between the GPU and the heatsink. It is typically made from a base material, such as silicone, and mixed with thermally conductive materials like silver, copper, or ceramic particles.
As a medium for transferring heat, thermal grease has many advantages, such as excellent thermal conductivity, good lubricity, electrical insulation, good resistance to high and low temperatures, low viscosity and good construction performance. In addition, it also has the characteristics of low usage thickness and low thermal resistance, which makes it suitable for scenarios with high heat generation and close fit. It can be used to quickly transfer heat from the device to achieve good temperature control, thereby extending the service life of electronic components and improving their reliability. It can be placed on the heating device by dispensing, printing, etc. Thermal grease is a excellent thermal conductive composite material suitable for smaller gaps or no gaps.
Features and Advantages
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda thermal grease: 1-14.8W/mK
- Excellent thermal conductivity, high stability, excellent wetting performance
- Low thermal resistance, easy construction, and a very thin interface layer can be formed on the rough surface
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental requirements
Applications
High-Performance Systems: Commonly used in high-end gaming PC, workstations, and servers where superior thermal performance is required.
Overclocking: Essential for systems that are overclocked to ensure that additional heat is efficiently managed.


Thermal Gel
Thermal gel is a paste-like gap-filling thermal conductive material that can be cured at room temperature or high temperature. After curing, it appears as a flexible rubber elastomer. Thermal gel has the characteristics of excellent surface conformability and is suitable for contact surfaces with microscopic unevenness. The gel is formed with the shape of the structure and can be used to fully fill the gap. Since the gel has the characteristics of excellent insulation, pressure resistance, and high and low temperature resistance, it shows high reliability when used for a long time. In addition, it can also be used for automatic dispensing to achieve automated operations.
Features and Advantages
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda thermal gel: 2-8W/mK
- Excellent weather resistance, high and low temperature resistance, and insulation
- No sedimentation, no flow, it can be used to fill uneven gaps and can be used for automated dispensing
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental protection requirements
Applications
Consumer Electronics: Suitable for use in various electronic devices where high thermal performance and ease of use are desired.
Mobile Devices: Often used in smartphones and tablets to manage heat dissipation effectively.


Phase Change Material (PCM)
Phase change material is a specialized thermal interface material that change the state (from solid to liquid) at a specific temperature. This phase change allows it to adapt to varying thermal conditions, providing effective heat dissipation.
Phase change material is made of nano-grade high thermal conductive filler and phase change compound. It is used for the heat transfer interface between power consumption devices and heat sinks.
The state of the material changes at 52°C, from solid to liquid. Liquid phase change material can fully wet the surface of power-consuming devices and heat sinks to form an excellent heat conduction channel. It can also be used to achieve optimal heat dissipation performance of the heat sink and enhance the reliability of power devices.
Features and Advantages
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda phase change material: 8.5W/mk
- Phase change occurs at 52℃, from solid phase to liquid phase
- Low thermal resistance, excellent thermal conductivity and heat dissipation performance, good reliability
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental protection requirements
Applications
High-Performance Computing: Used in advanced cooling solutions for CPU and GPU in high-performance computing systems.
Electronics Cooling: Employed in various electronic devices to improve thermal management.

Consider the Key Factors
Thermal Conductivity
Definition: A measure of how well a material conducts heat. Higher values indicate better performance.
Recommendation: Look for materials with high thermal conductivity, especially if you're overclocking or pushing your GPU to its limits.
Application and Handling
Ease of Application: Thermal paste and pads vary in application difficulty. Thermal pads are easier to apply but may not always provide the best performance.
Durability: Consider how often you are willing to reapply the TIM. Some pastes need replacement every few years, while pads may last longer.
Compatibility
Surface Materials: Ensure that the TIM is compatible with both the GPU and heatsink materials. Thickness: For pads, ensure they are thick enough to fill gaps but not so thick that they prevent proper contact.
Thermal Performance
Performance Requirements: If you’re using a standard GPU setup, a good quality thermal paste or pad is usually sufficient. For high-performance or overclocked systems, consider high-end thermal paste.
Application Techniques and Best Practices
Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is crucial for effective thermal management. Both the GPU and heatsink surfaces should be clean and free of dust, old thermal material, or contaminants. Use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth to clean the surfaces before applying any thermal interface material.
Application of Thermal Pads
Thermal pads are straightforward to apply. Simply place the pad onto the GPU or heatsink surface, ensuring proper alignment. Avoid stretching or bending the pad, as this can affect its performance.
Application of Thermal Grease
When applying thermal grease, use a small amount and spread it evenly across the surface. A thin, even layer is ideal, as excessive paste can lead to inefficiencies and potential overheating. Common application methods include the dot method, line method, or spread method.
Application of Thermal Gel
Thermal gel application is similar to thermal grease. Apply a small amount of gel to the GPU surface and spread it evenly. Ensure that the gel covers the entire surface area for optimal heat transfer.
Reapplication and Maintenance
Thermal interface materials should be checked periodically, especially in high-performance or overclocked systems. Reapply thermal grease or gel if signs of degradation are noticed, such as increased temperatures or decreased performance.
Conclusion
Effective GPU heat dissipation is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in modern computing systems. Thermal conductive interface materials, including thermal pads, thermal grease, thermal gel, and other specialized materials, play a vital role in this process. By understanding the properties, applications, and best practices for these materials, users can make informed decisions to manage GPU heat effectively and maintain system stability. Advances in thermal interface materials and cooling technologies continue to evolve, promising even more efficient solutions for future computing demands.









