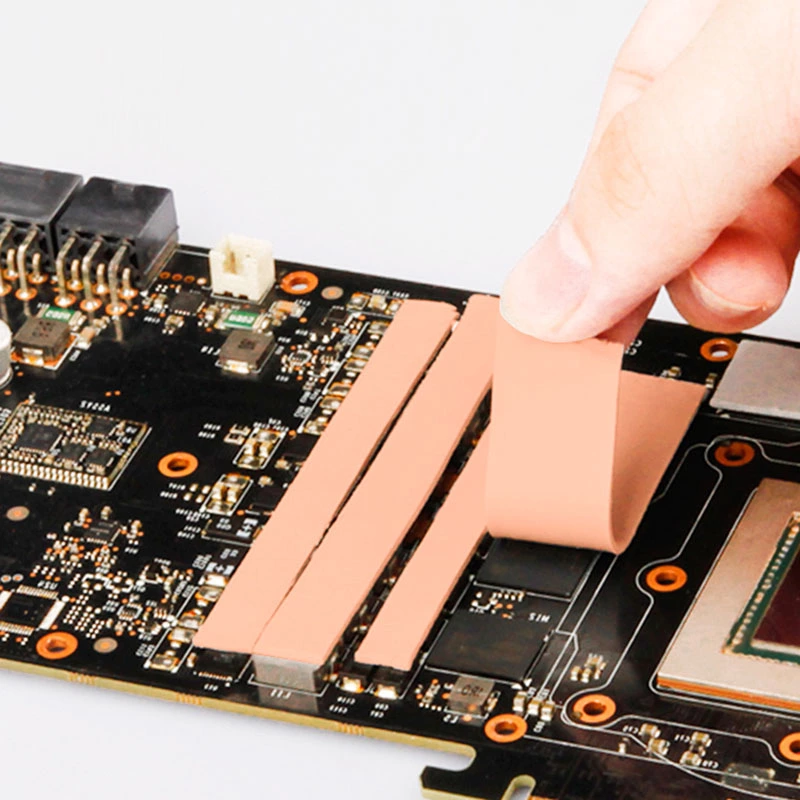
When it comes to managing heat in electronic devices such as computers, graphics cards, or other high-performance components, thermal interface materials (TIMs) play a crucial role in ensuring effective heat transfer between the heat source (like a CPU or GPU) and the heat sink. Thermal putty and thermal pad are the most common TIM materials. Both are used to improve heat transfer between heat sources and heat sinks, but they differ significantly in terms of appearance, application, and use cases.

Thermal Putty vs Thermal Pad,which is better?
When it comes to managing heat in electronic devices such as computers, graphics cards, or other high-performance components, thermal interface materials (TIMs) play a crucial role in ensuring effective heat transfer between the heat source (like a CPU or GPU) and the heat sink. Thermal putty and thermal pad are the most common TIM materials. Both are used to improve heat transfer between heat sources and heat sinks, but they differ significantly in terms of appearance, application, and use cases.
In this article, we will explore the differences between thermal putty and thermal pad, their respective advantages, how to choose the right one for your needs, and how to properly apply them to achieve optimal thermal performance.
What is Thermal Putty?
Thermal putty is a highly viscous, semi-solid substance designed to fill the microscopic gaps and irregularities between two surfaces. It is typically made from a combination of thermally conductive materials (like aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride) suspended in a binder or a polymer matrix. The result is a thick, paste-like material that has good heat transfer properties.
Advantages of Thermal Putty:
High Thermal Conductivity: Thermal putty typically offers excellent thermal conductivity, especially those containing high-quality metal particles.
- Fills Irregular Gaps: Its paste-like consistency allows it to conform to various shapes and fill gaps of different sizes, providing more complete contact between the heat source and the heatsink, which is ideal for uneven or poorly-aligned surfaces.
- Customizable: You can apply more or less putty to control the thickness of the layer, making it more versatile for different setups.
- Long-Term Durability: Thermal putty, especially high-end versions, tends to maintain its thermal properties over extended periods and high temperatures, which makes it more reliable for long-term applications.
FEHONDA Thermal Putty
- Good thermal conductivity (16-18 W/mk) 12g/50g/100g
- Good softness and is conformable at low pressure, softness results in low stress on board components
- Good dielectric properties
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental protection requirements
- Can replace thermal conductive silicone pad
FEHONDA LTP81 Thermal Putty
===>Click Here to Buy LTP81 Thermal Putty

FEHONDA LTP65 Thermal Putty
===>Click Here to Buy FEHONDA LTP65 Thermal Putty

What is a Thermal Pad?
A thermal pad is a solid material (usually made of silicone and thermally conductive fillers). Unlike thermal putty, thermal pads are typically cut into specific sizes and shapes to fit between heat-generating components and heatsinks. They are often used in mass production environments because they are easy to handle and apply without making a mess
Advantages of Thermal Pads:
- Ease of Use: Thermal pads are easy to apply and require no mixing or special tools. You simply peel off the protective layer and place them directly on the surface.
- Clean and Convenient: Since they are solid, thermal pads are much cleaner than thermal putty, reducing the risk of spillover onto other components.
- Consistent Thickness: Thermal pads provide a uniform and consistent thickness, ensuring that there are no air gaps between components.
- Electrical Insulation: Provides good electrical insulation, making them suitable for electronic devices where voltage is present across the interface.
FEHONDA Thermal Pad
===>Click Here to Buy FEHONDA Thermal Pad
- Thermal conductivity of Fehonda thermal pad: 1.5-15.0W/mk
- Low thermal resistance, excellent thermal conductivity, good weather resistance
- Self-adhesive, good fit, easy to assemble
- Soft, good compressibility, high reliability in long-term use
- UL94 V-0 flame retardant, meets RoHS environmental protection requirements
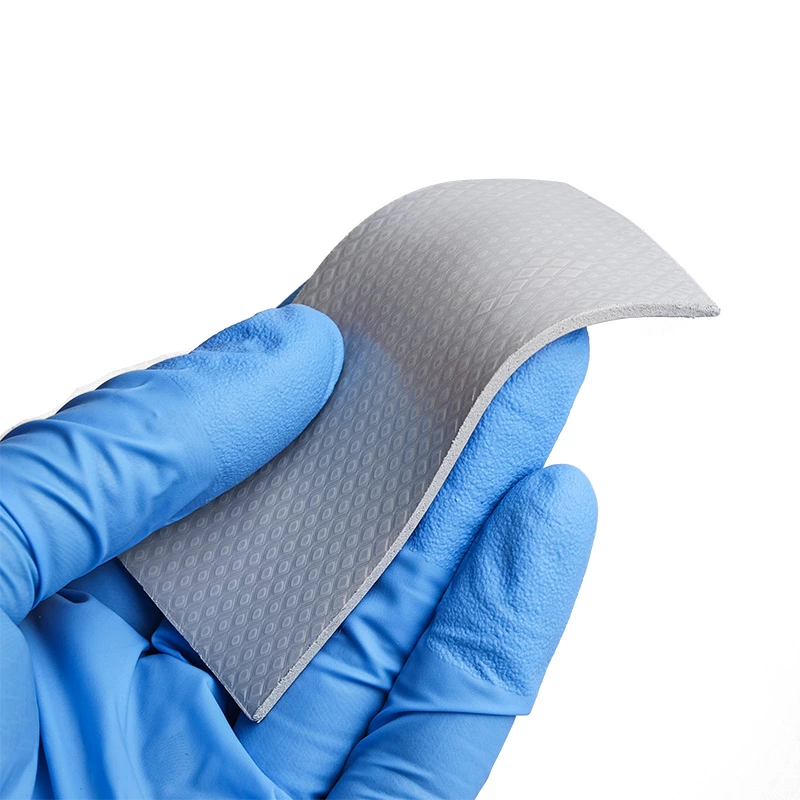
Thermal Putty vs. Thermal Pad: Key Differences
| Feature | Thermal Putty | Thermal Pad |
| Appearance | Viscous paste | Solid material |
| Application | Good moldability | Easy to apply |
| Thickness Control | Customizable (more or less putty can be applied) | Pre-defined thickness |
| Use Cases | High-performance, custom applications | Mass production, easier maintenance |
How to Choose Between Thermal Putty and Thermal Pad
Choosing between thermal putty and thermal pads depends largely on your specific needs, the application environment, and performance requirements. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Performance Requirements:
Thermal Putty is the better choice if you need high thermal conductivity for demanding applications, such as high-end gaming PCs, overclocked CPUs, or high-performance graphics cards.
Thermal Pads are ideal for general consumer electronics, mass-produced devices, or situations where ease of application and cleanliness are more important than peak thermal efficiency.
- Ease of Application:
If you prefer a simple, no-mess solution, thermal pads are more convenient. They are easy to apply and typically require less time and effort.
For custom setups or where you need to fill gaps and irregularities, thermal putty provides more flexibility, though it requires more care during application.
- Surface and Setup:
If the surfaces of your components are uneven or irregular, thermal putty is more suitable because it can fill those gaps and provide a more complete seal.
For well-aligned surfaces, thermal pads should work just fine and are less likely to create mess or require excessive cleanup.
How to Apply Thermal Putty and Thermal Pads
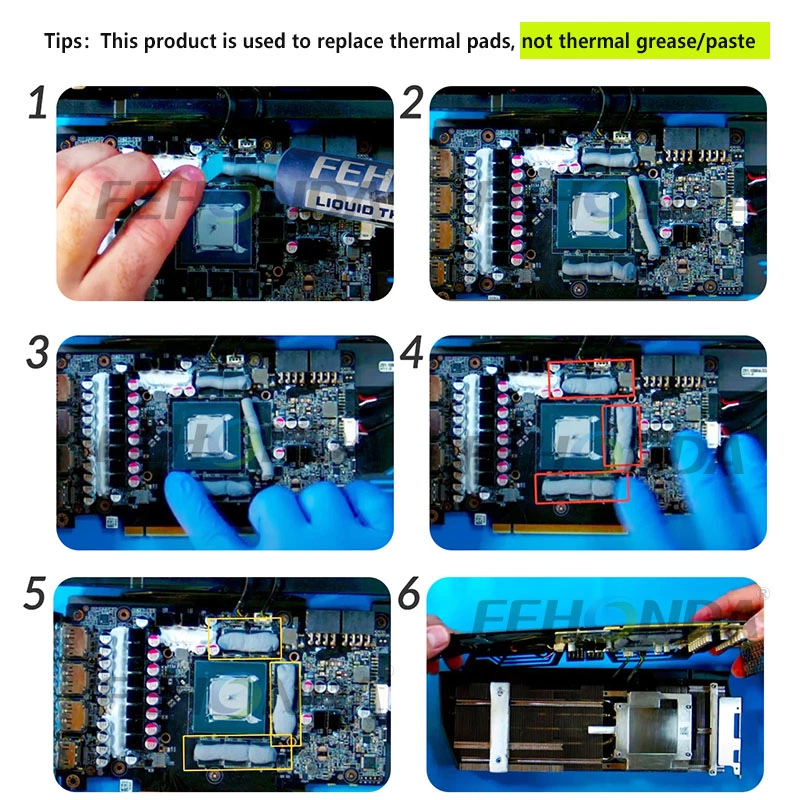
Applying Thermal Putty:
- Clean the Surfaces: Make sure the surface clean and free from dust and old thermal materials.
- Apply the Putty: Using a small spatula or your fingers (gloved), apply a suitable, even layer of thermal putty to the surface.
- Spread Evenly: Ensure the putty covers the entire contact area without spilling over the edges. If necessary, use a spreading tool to ensure an even layer.
- Reattach the Heatsink: Once applied, carefully place the heatsink onto the putty and secure it. Press down gently to spread the material and remove any excess.
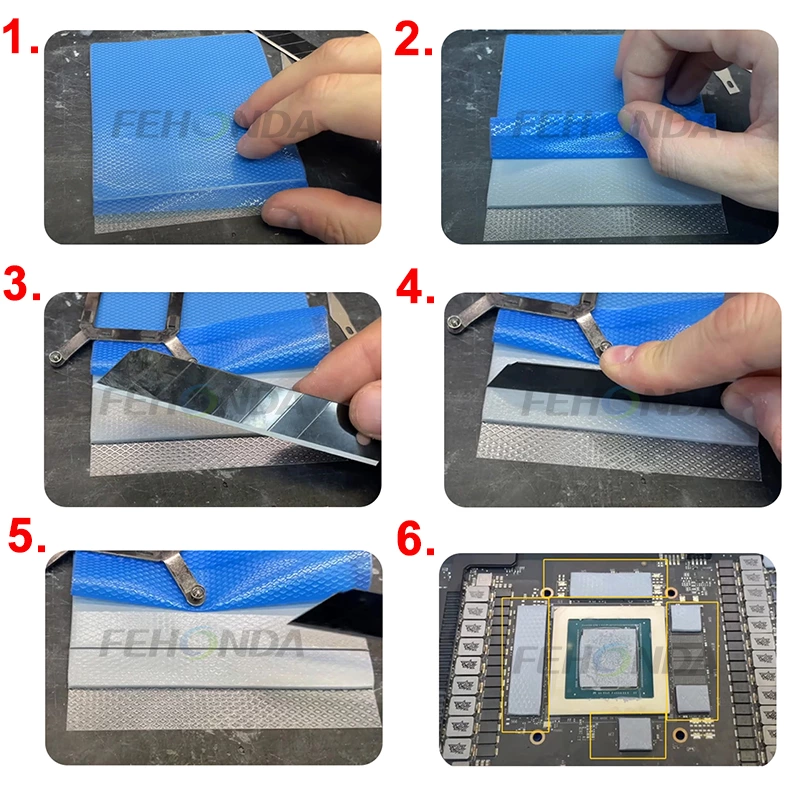
Applying Thermal Pads:
- Clean the Surfaces: Similar to thermal putty, ensure the surfaces are free of dust, debris, and old thermal material.
- Peel the Pad: Remove the protective film from the thermal pad.
- Place the Pad: Simply place the thermal pad over the surface, aligning it with the contact area.
- Attach the Heatsink: Gently place the heatsink over the pad and apply light pressure to ensure good contact. No need to spread or adjust the material.
- Press and Secure: Once the heatsink is secured, ensure the pad is in full contact.
Conclusion
Choosing between thermal putty and thermal pads depends on your specific needs, application type, and desired performance. If you think about molding the interface material into various shapes and filling uneven gaps and have the expertise to apply it correctly, thermal putty is an excellent choice. On the other hand, if you need an easy, clean solution with consistent performance, thermal pads are the way to go.
By understanding their differences and following proper application methods, you can ensure that your electronic components stay cool and perform optimally for the long term.